Heap Files
Overview
Heap files are:
- Sequence of pages containing tuples.
- No inherent ordering of tuples.
- Pages may contain free space from deleted tuples.
- Does not generally involve overflow pages.
Selection in Heaps
No strategy other than a linear scan.
Insertion
Main strategy:
- Append tuple to file in last page.
Alternative strategy:
- Find any page from for the relation with enough space.
- Preferably a page already loaded into a buffer.
PostgreSQL strategy:
- Use last updated page of relation in buffer pool if enough space.
- Otherwise, search buffer pool for page with enough space.
- Assisted by free space map (FSM) associated with each table.
Oversized Tuples
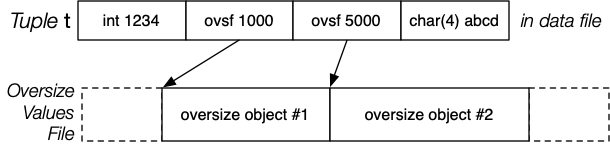
for attribute in t:
if attribute not oversized:
continue
off = appendToFile(overflow_file, attribute)
attribute = (OVERSIZE, off)
# insert into buffer as before
PostgreSQL Implementation
heap_insert(Relation, relation, HeapTuple newTup, CommandId cid, ...)
- Finds page which has enough free space for
newtup. - Ensures page loaded into buffer pool and locked.
- Copies tuple data into page buffer, sets
xmin, etc. - Marks buffer as dirty.
- Writes details of insertion in transaction log.
- Returns OID of new tuple if relation has OIDs.
Deletion in Heaps
rel = openRelation("RelationName", READ | WRITE)
for page_num page in enumerate(pages(rel)):
n_deletions = 0
for tuple_num, _tuple in enumerate(tuples(page)):
if satisfies_condition(_tuple):
n_deletions += 1
delete_record(buf, tuple_num)
if n_deletions > 0:
put_page(rel, page_num, buf)
if n_deletions > 0 and unique:
break
PostgreSQL Implementation
heap_delete(Relation rel, ItemPointer tid, ..., CommandId cid, ...)
- Gets page containing tuple
tidinto buffer pool and locks it. - Sets flags, commandID and
xmaxin tuple; dirties buffer. - Writes indication of deletion to transaction log.
Vacuuming eventually compacts space in each page.
Updates in Heaps
Analysis for updates similar to deletion:
- Scan all pages.
- Replace any updated tuples (within each page).
- Write affected pages to disk.
Complication: new tuple larger than old version (too big for page). Solution: delete, reorganise free space, then insert.
PostgreSQL Implementation
heap_update(Relation rel, ItemPointer otid, HeapTuple newtup, ..., CommandId cid, ...)
- Essentially does
delete(otid), theninsert(newtup). - Also sets old tuple’s
ctidfield to reference new tuple. - Can also update-in-place if no referencing transactions.
Heaps in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL stores all table data in heap files by default.
Typically there are also associated index files.
If a file is more useful in some other form:
- PostgreSQL may make a transformed copy during query execution.
- Programmer can set it via
create index ... using hash.
PostgreSQL “heap file” may use multiple physical files.
- Files are named after the
OIDof the corresponding table. - First data file is called simply
OID. - If size exceeds
1GB, create a fork calledOID.1. - Add more forks as necessary.
- Other files:
- Free space map (
OID_fsm), visibility map (OID_vm). - Optionally, TOAST File (if table has large varlen attributes).
- Free space map (