Scanning
Simple Implementation (No Overflow Pages)
select * from Rel;
Abstract implementation:
for _tuple in rel:
result.add(_tuple)
Operational implementation:
for page in pages(rel):
for _tuple in page:
result.add(_tuple)
Cost = read every data page once = b
Implementation with Overflow Pages
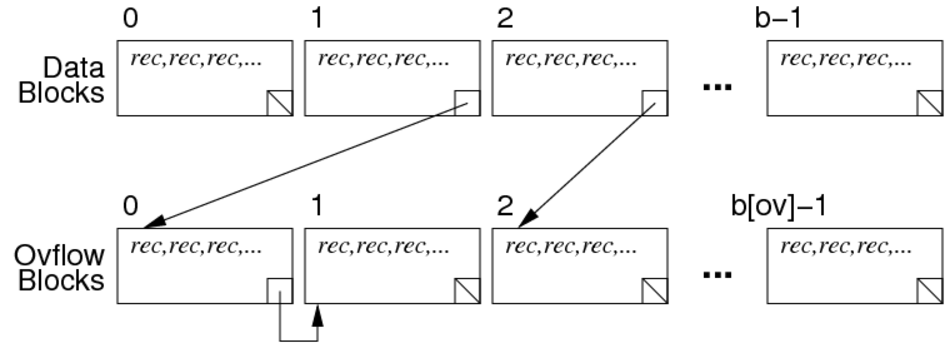
Implementation becomes:
for page in pages(rel):
for _tuple in page:
result.add(_tuple)
for overflow_page in overflow_pages(p):
for _tuple in overflow_page:
result.add(_tuple)
Cost = read each data page and each overflow page once = b + b_Ov where b_Ov is the total number of overflow pages.
Selection via Scanning
select * from Employee where id = 762288;
Overview of scan process:
for page in pages(Employee):
for _tuple in p:
if _tuple.id == 762288:
return _tuple
Cost analysis for one searching in unordered file:
- Best case: read one page, find tuple.
Cost_min = 1.
- Worst case: read all
bpages, find in last (or don’t find).Cost_max = b.
- Average case: read half of the pages (
b / 2).Cost_avg = b / 2.
Iterators
Scan s = start_scan(Relation r, ...)
- Commence a scan of relation
r. Scanmay include condition to implementWHERE-clause.Scanholds data on progress through file (e.g. current page and current tuple).
Tuple next_tuple(Scan s)
- Return
Tupleimmediately following last accessed one. - Return
NULLif no moreTuples left in the relation.
Example usage:
Db db = openDatabase("myDB");
Relation r = openRelation(db, "Employee", READ);
Scan s = start_scan(r);
Tuple t;
while ((t = next_tuple(s)) != NULL) {
char *name = getStrField(t, 2);
printf("%s\n", name);
}
Scan Struct
Possible implementation:
typedef ScanData *Scan;
typedef struct {
Relation rel;
Page *page; // Page buffer
int curPID;
int curTID;
} ScanData;
next_tuple() Function
Possible implementation:
Tuple next_tuple(Scan s)
{
if (s->curTID >= nTuples(s->page)-1) {
// get a new page; exhausted current page
s->curPID++;
if (s->curPID >= nPages(s->rel))
return NULL;
else {
s->page = get_page(s->rel, s->curPID);
s->curTID = -1;
}
}
s->curTID++;
return get_tuple(s->rel, s->page, s->curTID);
}
Relation Copying
-- Copies data from one table to a new table.
create table T as (select * from S);
Implementation with Iterators:
// make empty relation T
Scan s = start_scan(S);
Tuple t;
while (t = next_tuple(s)) {
// insert tuple t into relation T
}
Implementation with Page operations:
Relation in; // relation handle (incl. files)
Relation out; // relation handle (incl. files)
int ipid, opid, tid; // page and record indexes
Record rec; // current record (tuple)
Page ibuf, obuf; // input/output file buffers
in = openRelation("S", READ);
out = openRelation("T", NEW|WRITE);
clear(obuf); opid = 0;
for (ipid = 0; ipid < nPages(in); ipid++) {
ibuf = get_page(in, ipid);
for (tid = 0; tid < nTuples(ibuf); tid++) {
rec = get_record(ibuf, tid);
if (!hasSpace(obuf, rec)) {
put_page(out, opid++, obuf);
clear(obuf);
}
insert_record(obuf,rec);
} }
if (nTuples(obuf) > 0) put_page(out, opid, obuf);
Scanning in PostgreSQL
Iterator data/operations:
HeapScanDes: struct containing iteration state.scan = heap_beginscan(rel, ..., nkeys, keys.tup = heap_getnext(scan, direction).heap_endscan(scan): frees up struct.res = HeapKeyTest(tuple, ..., nkeys, keys).
typedef HeapScanDescData *HeapScanDesc;
typedef struct HeapScanDescData
{
// scan parameters
Relation rs_rd; // heap relation descriptor
Snapshot rs_snapshot; // snapshot ... tuple visibility
int rs_nkeys; // number of scan keys
ScanKey rs_key; // array of scan key descriptors
...
// state set up at initscan time
PageNumber rs_npages; // number of pages to scan
PageNumber rs_startpage; // page # to start at
...
// scan current state, initally set to invalid
HeapTupleData rs_ctup; // current tuple in scan
PageNumber rs_cpage; // current page # in scan
Buffer rs_cbuf; // current buffer in scan
...
} HeapScanDescData;
Scanning in other File Structures
Previous examples are for heap files.
- Simple, unordered, maybe indexed, no hashing.
Other access file structures in PostgreSQL:
btree, hash, gist, gin.- Each implements:
startscan, getnext, endscan.insert, delete(update = delete + insert).- Other file-specific operators.